In our previous article, we outlined the benefits of short-term ‘work from anywhere’. We will now focus on the advantages of introducing flexible hours and days.
In a recent survey, HR professionals in the US advised that:
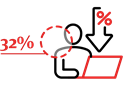 |
- 32% of their organisations offer a compressed workweek, and
|
 |
- 50% offer flextime during core business hours.1
|
| |
|
 |
Flexible working hours “can be successful when managers liaise with staff, likely on an individualised basis, about how the set-up would work best for them.”2 |
 |
This “employee-driven approach to flexible working that empowers employees to choose where, when and how they work”3 has been termed hyper-personalisation, accommodating the “different styles and different needs”4 of employees. |
Microsoft believes that successful organisations will “find ways to accommodate different work styles as the path to helping everyone to do their best work.”4
This paper will focus on two main initiatives:
 |
- A four-day workweek with reduced hours and no reduction in pay, and
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
Following a four-day workweek trial in 2021, more than 80% of employees of San Francisco-based Bolt said they had been more productive and efficient with their time, combined with an improvement in their work-life balance5. |
 |
Bolt has now implemented the four-day workweek permanently and has since “been inundated with resumes and emails from people interested in working for the company.”6 |
 |
Introducing a four-day week is not a new initiative. In 2018, Perpetual Guardian moved all New Zealand employees “from a five-day to a four-day week…while maintaining their pay.”7 This move “was very successful (as) productivity increased and stress declined.”8 |
 |
This initiative has been recently gaining traction, and a four-day, 32-hour workweek without loss of pay is the most popular four-day workweek option globally.9 |
 |
In the US and Canada, 30 organisations have signed up to trial a four-day workweek coordinated by four Day Week Global,5 an organisation co-founded by A Barnes (the founder of Perpetual Guardian NZ).8 |
 |
In the UK, 30 organisations have signed up for “a four-day week trial run by think tank Autonomy along with Cambridge and Oxford Universities and Boston College (that) will measure employee productivity.”10 |
Belgium, Spain, Scotland, and Iceland have trialled, or will trial, a four-day workweek or reduced weekly hours.8,10,11
 |
An alternative rationale for the four-day workweek is that it can also suit the organisations financially unable to “compete for talent through compensation” as it gives them the option to “shorten the work week rather than increase pay.”12 |
Another flexible hours initiative is to introduce additional paid leave for employees. Some examples are:
- Finder has granted five extra days paid leave “for life’s big events.”13
- Iress has introduced leave that enables employees “to take six long weekends every year.”13
- Monzo offers employees “three months of paid leave for every four years they work.”14
No matter how working hours flexibility is introduced, successful organisations will focus on employee output, on the work that matters, and on reducing (or eliminating) unnecessary, time-consuming work.
“We should not care about how many days or hours anyone works. Every job or task should have objective metrics, which are output based, and if an employee can perform those metrics in two days, so be it.”15
 |
According to Bolt, the key to making a four-day week successful is “to work more efficiently,” as “a lot of companies operate with a lot of work theater…with countless meetings, countless documents, countless presentations.”5 |
Holding too many meetings “can be highly stressful and tiring, and productivity and quality take a hit when employees tune out, become demotivated and lose valuable heads-down work time.”16
In summary, significant benefits can be gained by offering flexibility in working hours and days to suit the needs and preferences of your employees.
Are the days of the five-day week over? Not yet - but the four-day workweek movement is gaining traction worldwide. The four-day work week is “a very sensible, rational business practice that improves your productivity and profitability by giving your staff more time off.”17
Norton Rose Fulbright assists organisations to efficiently and effectively address the legal aspects of the new global work environment, including flexibility in working hours. Please reach out if we can assist your organisation in this respect.
Our next paper will consider how to make ‘work from anywhere’ work better.













